How Double-Glazed Windows Work: A Deep Dive into Energy Efficiency
In the world of home improvement and energy efficiency, double-glazed windows have emerged as a game-changing technology for modern homes and buildings. As a trusted supplier of aluminum alloy door and window products, we’re here to shed light on how these windows work and why they are essential for optimizing thermal insulation and reducing energy costs. Let’s dive into the science behind their efficiency and explore the role of key technologies like Low-E coatings and advanced window technology.
1. Understanding Double-Glazed Windows: The Basics
Double-glazed windows, also known as insulated glass units (IGUs), feature two panes of glass separated by a spacer bar and sealed to create a hermetic cavity. This cavity is filled with air or insulating gases like argon or krypton, which act as barriers against heat transfer. The resulting structure significantly reduces thermal conductivity, making these windows far more efficient than traditional single-pane options.
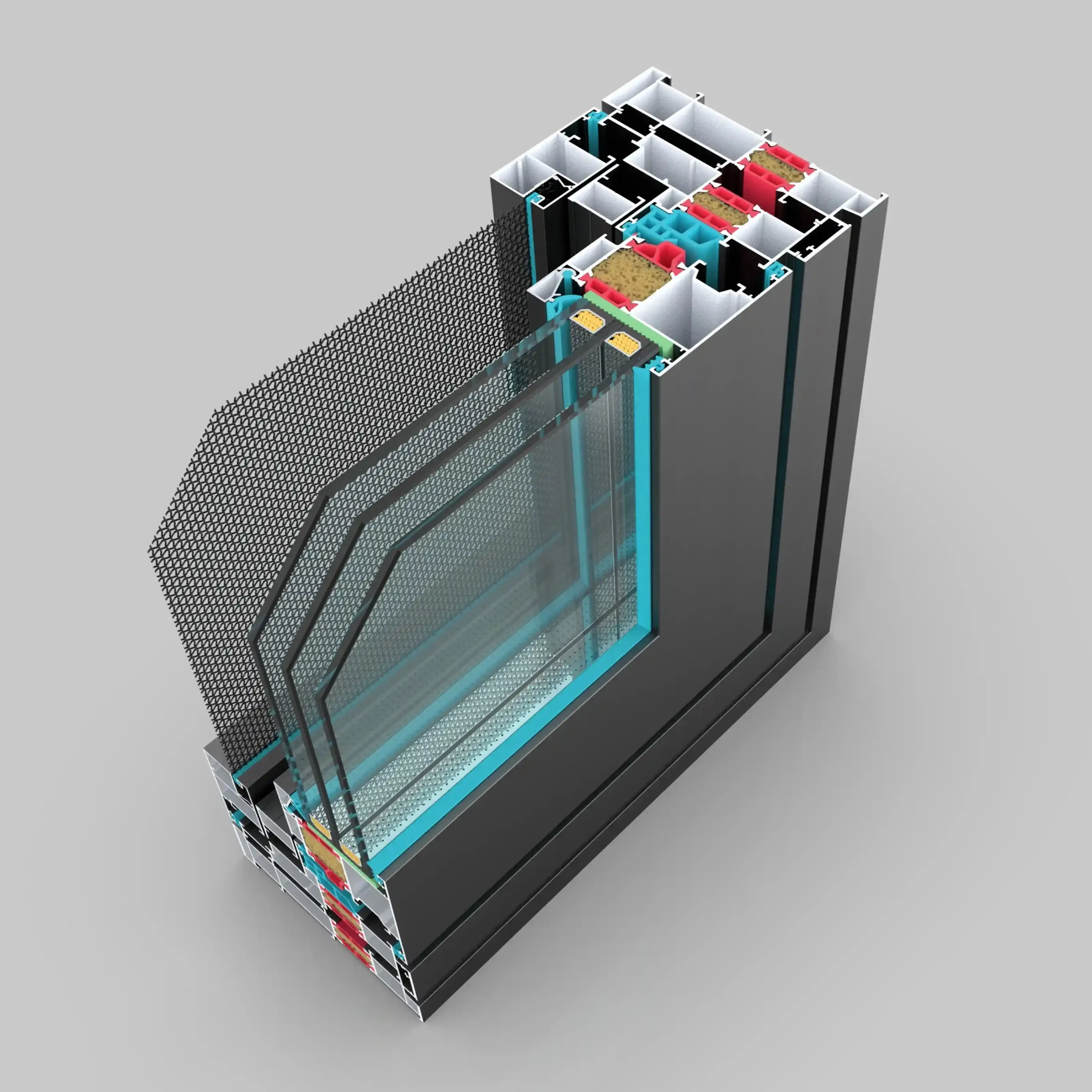
2. The Science of Thermal Insulation: U-Values vs. K-Values
To understand the energy-saving potential of double-glazed windows, we must first grasp the concepts of U-values and K-values. Both metrics measure a material’s ability to conduct heat:
- U-Value (U-factor): Measures the overall heat transfer rate of a window assembly. Lower U-values indicate better insulation (e.g., U=1.0 W/m²K is more efficient than U=3.0).
- K-Value (Thermal Conductivity): Measures the heat transfer rate of a single material (e.g., glass or aluminum). It’s used to calculate U-values in combination with other components.
Key Comparison:
- Single Pane Glass: Typically has a high K-value (around 6 W/m²K), resulting in a U-value of 5.0–6.0, meaning significant heat loss/gain.
- Double-Glazed Windows: With air or gas-filled cavities and improved frames, U-values can range from 1.5 to 2.5, reducing heat transfer by up to 50%.
Experimentally Proven Efficiency: Studies show that double-glazed windows with argon gas fill and Low-E coatings can achieve U-values as low as 1.1 W/m²K, outperforming single-pane glass by over 4x in thermal resistance.
3. Low-E Glass: The Energy Efficiency Booster
While double-glazing alone improves insulation, the addition of Low-E (low emissivity) coatings takes efficiency to the next level. Low-E glass features a microscopically thin layer of silver or other metals, which:
- Reflects radiant heat while allowing visible light to pass through.
- In winter, it traps indoor heat, reducing heat loss.
- In summer, it blocks solar heat gain, keeping interiors cooler.
Energetic Impact Comparison:
- Ordinary Double-Glazed Windows (without Low-E): U≈2.0, offering basic thermal protection.
- Low-E Double-Glazed Windows: U≈1.2–1.5, with up to 70% reduction in solar heat transfer.
Real-World Energy Savings: Lab tests and field studies demonstrate that homes with Low-E double-glazed windows can lower summer AC energy consumption by 30% compared to those with standard double-glazed windows. This translates to substantial cost savings and environmental benefits.

4. Window Technology Advancements: Beyond the Basics
Modern double-glazed systems leverage additional technologies to maximize efficiency:
- Multilayer Coatings: Some windows use dual Low-E coatings for even better performance in extreme climates.
- Aerogel Fill: Replacing gas with aerogel (a lightweight, solid insulator) can achieve U-values as low as 0.5 W/m²K, ideal for passive houses.
- Smart Tinting: Electrochromic glass can dynamically adjust transparency, further regulating solar heat intake.
5. Environmental and Economic Benefits
Investing in double-glazed windows with advanced features pays off in multiple ways:
- Energy Cost Reduction: Annual savings on heating/cooling bills can range from 15% to 40% depending on climate and window specs.
- Carbon Emissions Cut: Reduced energy use directly lowers your home’s carbon footprint.
- Property Value Boost: Energy-efficient upgrades enhance resale appeal and marketability.
- Comfort Enhancement: Consistent indoor temperatures and noise reduction create a healthier living environment.
6. Maintenance: Keeping Your Windows Efficient
To prolong the performance of double-glazed windows:
- Clean Regularly: Use non-abrasive cleaners to maintain glass clarity and frame integrity.
- Inspect Seals: Check for gaps or moisture between panes, which indicate seal failure.
- Avoid Extreme Temperature Variations: Rapid heating/cooling can stress the unit, affecting longevity.
- Professional Inspections: Schedule annual checks to ensure gas fill integrity and frame stability.

Conclusion
Double-glazed windows are more than just a modern aesthetic choice—they are a strategic investment in energy efficiency and long-term savings. By leveraging advanced window technology (Low-E coatings, gas fills, and optimized designs), these systems excel at thermal insulation, outperforming traditional glass by orders of magnitude. Whether you aim to reduce your carbon footprint, lower utility bills, or enhance home comfort, upgrading to double-glazed windows is a step toward a smarter, more sustainable future.

